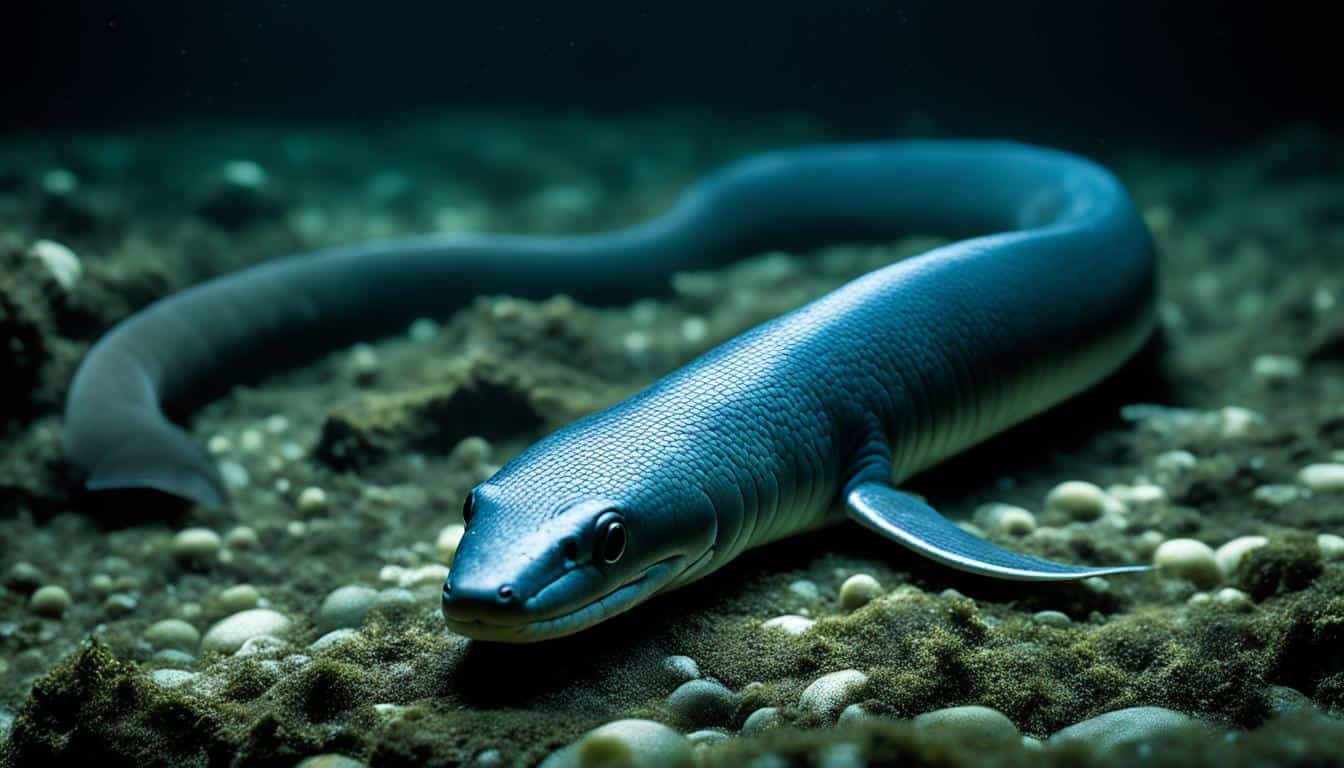
The electric eel (Electrophorus electricus) is a fascinating creature known for its unique abilities. Many people wonder if electric eels are endangered. Currently, they are not considered endangered, but their situation is still concerning.
These eels live in freshwater areas near the Amazon and Orinoco rivers in South America. Even though they face threats from environmental changes, they are not yet endangered. Conservationists keep a close eye on their numbers and the health of their habitats.
Understanding Electric Eels
Electric eels are fascinating creatures that belong to the knifefish family. They have unique electric eels characteristics that grab the attention of researchers and fans. These fish are not true eels but are more related to carp and catfish. They can grow up to 2 meters long and weigh about 20 kilograms.
Their bodies are long and thin without scales. They come in colors like purple, gray, blue, and black. This makes them stand out in the water.
Classification and Characteristics
Electric eels are classified as remarkable creatures. They live alone and can breathe air, which helps them survive in places with little oxygen. They have a special ability to make electricity thanks to cells called electrocytes.
The main organ for making electric signals is big and takes up about 80% of their body length. The Hunter’s organ helps deliver shocks, and the Sach’s organ is key for finding their way around.
Electric Organs: How They Work
The electric organs of electric eels are crucial for their survival. These organs can send out low-voltage signals for finding their way and talking to others. They can also produce high-voltage shocks for defense and catching prey.
Each electric organ has many electrocytes stacked together like batteries. This shows how electric eels have evolved to be so unique in the electric eels classification.
| Electric Organ | Function | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Main Organ | Electric shock and communication | Dominates in size, contributing to 80% of body length |
| Hunter’s Organ | Supplement shock delivery | Works in conjunction with the Main Organ for high-voltage output |
| Sach’s Organ | Electrolocation | Allows navigation by sensing electrical fields |
Are electric eels endangered?
Understanding the electric eels’ current status helps us see the threats they face and their chances of survival. They are not yet endangered, but their conservation is still important. This is because changes in the environment are affecting their homes.
Current Conservation Status
Electric eels are doing well in many freshwater places. But, they could face dangers from losing their homes and changes in the climate. We need ongoing research to make sure their homes are safe.
Geographical Range and Habitat
Electric eels live in parts of South America, like Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and some areas of the Guianas. They like slow-moving waters, such as ox-bow lakes, pools, and flooded forests. Knowing where they live helps us understand how changes in the environment might affect them. These changes could make it harder for them to survive, especially during extreme weather.
| Country | Regions | Habitat Type |
|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Amazônia | Ox-bow lakes, flooded forests |
| Colombia | Amazon Basin | Slow-moving rivers, wetlands |
| Venezuela | Orinoco River | Ponds, pools |
| Ecuador | Amazon River | Flooded areas |
| Guianas | Coastal regions | Freshwater wetlands |
Electric Eels Population Trends
The health of electric eels depends on their population trends. These trends change due to many factors affecting electric eels. These include habitat damage, climate changes, and human actions. Electric eels need open water to breathe air, which limits their area during dry times. This makes them very sensitive to environmental changes.
Factors Affecting Population Numbers
Many things affect the number of electric eels. Important factors affecting electric eels are:
- Environmental Quality: Pollution and losing their homes hurt their survival.
- Water Levels: Changes in water levels can block their breeding spots.
- Human Interference: Fishing, building cities, and cutting down trees harm their homes.
Breeding and Lifespan in the Wild
Knowing how long electric eels live in the wild is key to understanding their numbers. They usually live about 15 years in the wild. They breed mainly during the dry season. Males build nests with their saliva for the females to lay eggs in.
This special way of breeding helps them survive. Learning about this is crucial for saving their species.
Threats to Electric Eels
It’s important to understand the threats to electric eels to help protect them. These threats mainly come from losing their habitat due to human actions. By knowing these threats, we can take steps to protect their home and live in harmony with them.
Habitat Loss and Environmental Changes
Electric eels lose their habitat for many reasons, like deforestation and pollution. This makes it hard for them to find places to live and hunt. Pollution and environmental changes also make them more vulnerable to predators and competition.
Climate changes add to the problem by changing the ecosystem. This makes it harder for electric eels to survive.
Impact of Human Activities
Human activities like expanding farms, building cities, and industrial projects harm electric eels. This pollution and destruction of their homes hurt their ability to reproduce and survive. It’s crucial to understand these effects to protect electric eels.
We need to find ways for humans and wildlife to live together better. By changing human actions, we can help protect electric eels.
| Threat Type | Description | Impact on Electric Eels |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat Loss | Destruction of aquatic environments due to pollution and deforestation | Reduced breeding grounds and increased vulnerability |
| Climate Change | Fluctuations in climate affecting water quality and temperature | Altered habitat conditions leading to population stress |
| Pollution | Runoff from agriculture and industrial activities | Toxin exposure and habitat degradation |
| Overfishing | Decline in prey species and increased competition | Stress on electric eel populations and reduced food availability |
Electric Eels Conservation Status
The conservation of electric eels is a big task that needs help from many people. It’s important to protect these special animals and their homes. Laws that protect electric eels are key, stopping harm to their homes and keeping them clean. These rules help electric eels live in the wild and keep their numbers stable.
Legal Protections and Regulations
Laws are crucial for saving electric eels. They stop bad actions like cutting down forests and taking too much water. With these laws, electric eels have a better chance to survive and help the whole ecosystem. It’s up to leaders to make and enforce these laws to protect electric eels now and in the future.
Role of Local Communities in Conservation
Local communities are key in saving electric eels. Working with locals creates a sense of pride in nature and promotes green habits. By teaching people about electric eels and their role in nature, locals can help protect them. This teamwork makes conservation efforts stronger, ensuring a good future for electric eels and their homes.
FAQ
Are electric eels endangered?
Electric eels are not endangered yet. However, they face threats from losing their homes and environmental changes.
What is the current conservation status of electric eels?
Conservationists keep an eye on electric eels. They are not endangered, but their numbers show the bigger environmental problems.
Where do electric eels live?
Electric eels live in freshwater near the Amazon and Orinoco rivers in South America. You can find them in Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and parts of the Guianas.
What factors impact electric eel populations?
Many things affect electric eel numbers. These include changes in the environment, the availability of their homes, and humans moving into their space.
How do electric eels breed in the wild?
Electric eels breed during the dry season. Males make nests from their saliva for the females to lay eggs. They live about 15 years in the wild.
What threats do electric eels face?
Electric eels are threatened mainly by losing their homes due to deforestation, pollution, and human activities like farming.
How do human activities affect electric eels?
Human actions can damage their homes, making it harder for electric eels to find places to breed and hunt. This could threaten their survival.
What conservation measures are in place for electric eels?
Some places have laws and rules to protect forests and reduce pollution. Local communities also help by watching over the natural areas and spreading the word about electric eels.
How can local communities contribute to electric eel conservation?
Local communities are key to protecting electric eels. They help by keeping an eye on the environment and teaching others why electric eels are important.







